Introduction to RAG Model.

Combining Search and Generation for Reliable AI
We live in a time where AI can generate entire images or write full essays in a matter of seconds. It has become an incredibly powerful tool, helping us simplify tasks that would otherwise take hours to complete manually. While this makes AI smart and useful, the question is: how can we make it even smarter and more tailored to our specific needs?
This is where Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) models come into play. Traditional AI models are trained on vast amounts of general data. While this approach is effective, it isn’t always accurate for domain-specific use cases. To improve accuracy, we can fine-tune pretrained models using our own data—also known as a knowledge base—making them far more reliable and relevant to our context.
RAG models excel in both generation and retrieval from a defined knowledge base. For example, companies can train RAG models on their internal documentation, enabling the AI to provide precise answers and cite relevant references directly from their own knowledge sources. This approach is especially valuable for organizations like law firms or business enterprises that manage large volumes of raw data.
However, to fully appreciate how these models can be applied, it’s important to first understand how they work.
Understanding how RAG Models work
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) models work by generating responses from a pretrained large language model (LLM) using relevant information from a custom knowledge base. For example, if a user asks a chatbot a question about a product, the chatbot initiates a retrieval process. It uses vector embeddings to search the vector database and identify the most relevant information.
The retrieved data is then provided as context for the LLM, which uses it to generate a response that is more personalized, accurate, and efficient. Additionally, the generated response can be logged back into the knowledge base for future reference, creating a continuously improving system.
This entire process can be broken down into simpler, easier-to-understand steps, such as:
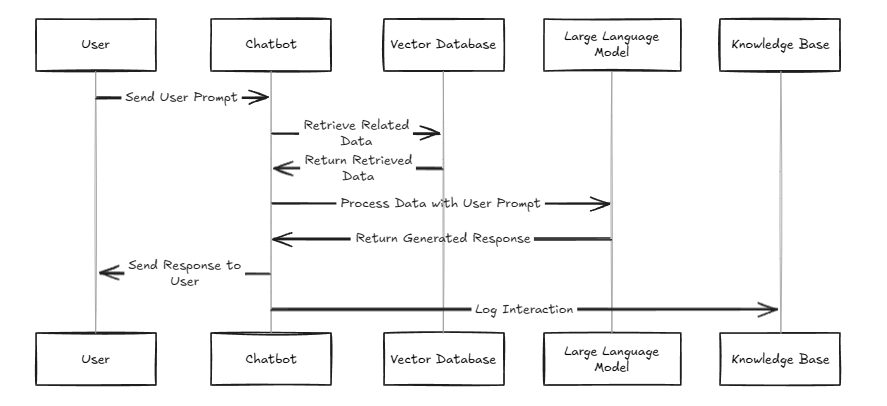
➡️ Retrieval from knowledge base
➡️ Context integration with the LLM
➡️ Response generation
➡️ Logging and feedback loop
This process gives us the most accurate and up-to-date information. Let’s dive a little into vector databases, LLMs, and what constitutes a knowledge base.
Vector Database
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) models rely on pulling relevant context from external data sources before generating responses, and this is where vector databases play a crucial role. Unlike traditional databases that search with exact matches, vector databases use embeddings—numerical representations of text, images, or other data—to capture semantic meaning.
This allows RAG models to retrieve contextually similar information, not just keyword matches, ensuring responses are more accurate and grounded. By efficiently handling high-dimensional embeddings, vector databases like Pinecone, Weaviate, Chroma DB, or FAISS enable scalable, low-latency retrieval.
In essence, they form the backbone of RAG pipelines, bridging the gap between vast unstructured data and intelligent, context-aware generation.
LLMs (Large Language Models)
Large Language Models (LLMs) form the generative engine at the heart of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. While LLMs excel at understanding and producing human-like language, they are limited by the knowledge encoded during training, which may be outdated or incomplete.
RAG bridges this gap by combining an LLM’s generative power with real-time retrieval from external knowledge sources. In this setup, the LLM doesn’t have to “remember everything”—instead, it uses the retrieved context to ground its responses in up-to-date, domain-specific information.
This synergy allows RAG models to produce outputs that are not only fluent and coherent but also factually relevant and context-aware.
Knowledge Base
In Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) models, the knowledge base acts as the trusted source of truth that supplements the Large Language Model’s capabilities. Instead of relying solely on what the LLM was trained on, a RAG pipeline queries a knowledge base (often powered by a vector database) to fetch the most relevant, semantically similar information.
This knowledge base can be built from documents, FAQs, research papers, product manuals, or any domain-specific content, making it adaptable to different use cases.
By grounding the LLM’s responses in this curated, constantly updatable knowledge base, RAG ensures outputs are more accurate, up-to-date, and context-specific.
Essentially, the knowledge base shifts the LLM from being a generalist to a domain expert, without the need for retraining.
Use Cases for RAG Models
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) models combine the creativity of Large Language Models (LLMs) with the factual accuracy of external knowledge sources. This makes them especially powerful in real-world applications where correctness, context, and up-to-date information are essential.
Here are five areas where RAG is making a big impact:
-
Customer Support Automation
Grounding chatbot responses in FAQs, manuals, and past tickets ensures customers get accurate, helpful answers instead of generic replies. -
Healthcare & Legal Research
RAG can pull evidence from medical journals or legal case databases, helping professionals quickly access reliable, domain-specific knowledge. -
Enterprise Knowledge Search
Employees can query vast internal repositories conversationally, glossing policies, reports, and documents instantly to improve productivity. -
Education & Training
Acting as a personalized tutor, RAG can fetch context-aware explanations from textbooks or training materials, enhancing learning experiences. -
Content Generation with Accuracy
From reports to marketing copy, RAG enables content creation that balances creativity with factual correctness by grounding outputs in trusted sources.
Improvements to the RAG Models
While Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has proven to be a powerful framework, researchers and practitioners are already exploring ways to make it faster, smarter, and more efficient.
One such advancement is Cache-Augmented Generation (CAG), which stores frequently retrieved results in a cache. Instead of performing repeated vector searches for the same or similar queries, the model can pull directly from cached responses, drastically reducing latency and computational costs while maintaining accuracy.
Other improvements include:
- Adaptive Retrieval – dynamically deciding how much external knowledge is needed for a given query, so simple questions don’t trigger heavy retrieval.
- Multi-Modal RAG – extending beyond text to include images, audio, or video as retrievable knowledge, making models more versatile.
- Knowledge Distillation in RAG – compressing and optimizing knowledge bases to speed up retrieval without sacrificing relevance.
- Hybrid Retrieval – combining keyword-based and vector-based search for higher precision in specific domains.
Conclusion
In summary, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) represents a significant leap in making AI both reliable and context-aware. By combining the generative strengths of large language models with the precision of curated knowledge bases, RAG delivers answers that are not only fluent but also factual and domain-specific. From customer support to healthcare, education, and enterprise search, its applications are vast and continually expanding.
With ongoing advancements like Cache-Augmented Generation, multi-modal retrieval, and hybrid search methods, RAG is evolving into a cornerstone technology for the future of AI. As organizations look to harness AI responsibly and effectively, adopting RAG models will be a crucial step toward building smarter, more trustworthy systems.